The global healthcare infrastructure utilizes private health insurance as a major element to offer families and individuals supplementary or alternative healthcare options to public services. The ability to understand differences between private health insurance and public healthcare as well as the factors affecting insurance costs and the pros and cons of each system makes choosing the best plan essential for informed healthcare decisions.
Main Differences Between Private Health Insurance and Public Healthcare Systems
Government entities usually fund and operate public healthcare systems which seek to deliver medical services to everyone. Public healthcare systems receive funding from tax revenues which allows them to deliver medical services at reduced or zero direct costs to patients (PMC). However, they may face challenges such as:
- Longer waiting times
- Resource constraints limit the availability of specialized treatments.
Private health insurance operates through for-profit companies which mandate premium payments from individuals who want coverage. Private plans often offer:
- A broader range of services
- Reduced waiting times
- Access to private healthcare facilities
- Private health insurance customers benefit from broader options for selecting their healthcare providers and treatment schedules.
Private insurance costs tend to be much higher while coverage details depend on the specific plan chosen.
Factors Affecting the Cost of Private Health Insurance
The cost of private health insurance premiums is determined by various factors, including:
1. Age
- Older individuals face higher insurance premiums because their health risks increase with age.
- People over the age of 50 can often pay premiums that are three times higher than those paid by younger adults for identical insurance coverage.
2. Location
- Geographical location significantly impacts premium costs.
- Local competition between insurers combined with state regulations and regional healthcare costs create these variations.
3. Tobacco Use
- People who use tobacco face higher insurance premiums because insurers associate tobacco use with greater health risks.
- Premiums for tobacco users can rise by up to 50% because insurers apply a tobacco surcharge compared to those who do not use tobacco.
4. Plan Type
- Health insurance premium costs depend on the structure of the plan.
- Insurance plans with reduced deductibles and out-of-pocket expenses usually charge higher premiums whereas plans with higher deductibles provide lower monthly rates but increase payment requirements when medical services are accessed.
5. Number of Dependents
- Adding family members to your insurance plan raises the premium because of the need to cover these extra people.
- The insurance plan becomes more expensive with each new dependent added.
6. Health Status
- The Affordable Care Act prevents insurance denial because of pre-existing health conditions but overall health status continues to affect insurance premium pricing.
- People with chronic health problems may require more healthcare services which can affect their insurance premium costs.
7. Gender
- Regional differences exist where premium costs vary between genders because of distinct healthcare usage patterns among males and females.
- Specific regions have rules that prevent insurance companies from setting prices based on gender.
8. Income Level
- Individuals and families with low incomes can obtain reduced premium costs through eligibility for subsidies and tax credits.
- Financial assistance programs exist to reduce the cost of health insurance for consumers.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Private Health Insurance Compared to Public Healthcare
Advantages:
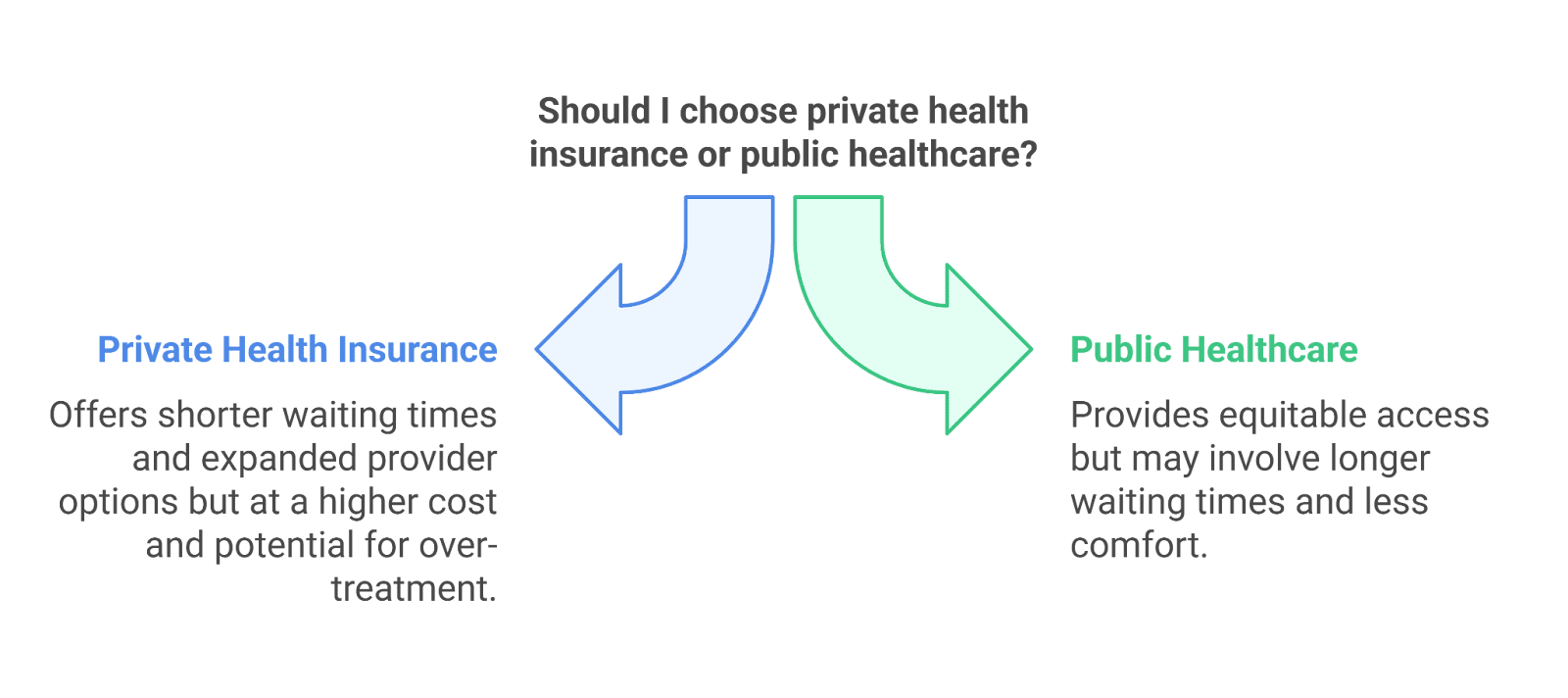
- Shorter Waiting Times: Private health insurance enables faster access to medical services which minimizes waiting times for both consultations and procedures.
- Expanded Provider Options: Private insurance policyholders enjoy access to a broader range of healthcare providers and facilities.
- Enhanced Comfort and Privacy: Private medical facilities can deliver better amenities such as private rooms and customized care services.
Disadvantages:
- Higher Costs: The high cost of private insurance premiums creates affordability problems for certain people.
- Potential for Over-Treatment: The financial motivations driving private healthcare providers can result in patients receiving unnecessary medical treatments or diagnostic tests.
- Equity Concerns: The dependence on private insurance systems leads to unequal healthcare access and results across different populations.
Choosing the Best Private Health Insurance Plan for Your Needs
Choosing the right private health insurance plan requires an assessment of your medical needs alongside your budgetary constraints. These steps will guide you through the process of making an informed decision:
1. Assess Your Healthcare Needs
- Evaluate your medical history and current health condition while projecting your future healthcare needs.
- Evaluate your healthcare requirements by looking at how often you see doctors, your prescription needs, upcoming medical procedures and your preferred healthcare providers.
2. Understand Plan Types
Learn about the basic kinds of health insurance plans available:
- Health Maintenance Organization (HMO): A PCP must provide referrals to access specialists and the plan costs less while offering limited flexibility.
- Preferred Provider Organization (PPO): PPOs let members choose their healthcare providers without needing referrals but require higher premium payments.
- Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO): Patients must use network providers except during emergencies and do not require referrals.
- Point of Service (POS): The POS model mandates specialist referrals from PCPs while permitting out-of-network services with increased expenses.
3. Compare Plan Networks
- Check that your chosen doctors and healthcare facilities belong to the plan’s provider network.
- When you use providers outside your insurance network you may face much larger out-of-pocket expenses.
4. Evaluate Costs
Review each plan’s cost components to understand their financial implications:
- Premiums: The monthly payment for the insurance plan.
- Deductibles: The out-of-pocket amount you must pay before your insurance begins to cover costs.
- Co-payments and Co-insurance: Patients pay either fixed amounts or service costs percentages after their deductible is met.
- Out-of-Pocket Maximum: Your insurance will cover all expenses after you reach the highest payment limit you have to make during each policy period.
5. Consider Coverage Benefits
- Evaluate insurance benefits that include prescription drug coverage along with mental health services and maternity care together with preventive services.
- Select a plan that offers services which match your individual health requirements.
6. Check for Additional Perks
- Certain plans provide wellness programs together with telehealth services and gym membership discounts.
- The plan’s value increases with these extra benefits.
7. Review Plan Ratings and Customer Feedback
- Evaluate service quality and customer satisfaction by researching plan ratings while reading customer feedback.
- The National Committee for Quality Assurance (NCQA) and state insurance department websites serve as dependable resources.
8. Seek Professional Advice
- Insurance brokers provide professional advice and help find customized insurance coverage solutions.
Conclusion: Private Health Insurance – A Path to Personalized Healthcare
Understanding private health insurance requires knowledge of how it differs from public healthcare and requires analysis of cost factors along with its benefits and drawbacks. PEO4YOU provides essential support to individuals and businesses who need customized health insurance options. PEO4YOU offers clients personalized health insurance solutions through human-centered claims management while ensuring cost transparency and access to an extensive provider network. Utilizing these resources allows individuals and organizations to select healthcare coverage options that deliver full benefits at reasonable costs through well-informed decision-making.

