The path to becoming a parent brings extraordinary happiness yet presents significant medical and financial obstacles. Pregnancy insurance provides essential healthcare coverage for expecting mothers and their families in the United States so they can get necessary care without facing excessive financial strain. The importance of obtaining pregnancy insurance has grown in 2024 because healthcare expenses rise while awareness of maternal health grows and healthcare systems become harder to navigate.
The Financial Burden of Pregnancy and Childbirth Represents an Urgent Concern
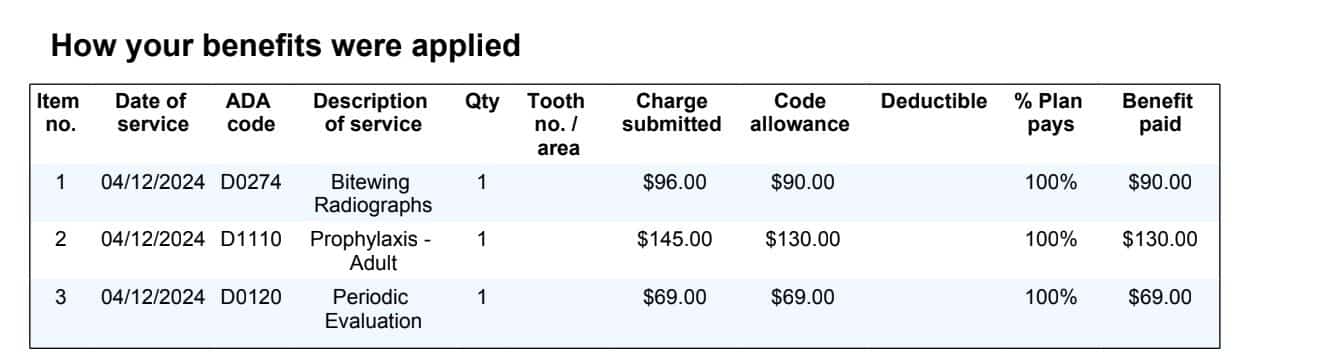
Families in the U.S. face an ongoing substantial financial burden when giving birth and this challenge grew more severe in 2024. FAIR Health reports that uncomplicated vaginal delivery costs between $5,000 and $11,000 while Cesarean sections range from $7,500 to $14,500. The provided figures typically omit related healthcare costs that include regular prenatal check-ups along with ultrasounds and postnatal care services.
The cost of both vaginal deliveries and C-sections in Florida stands between $8,000 and $13,000 placing the state among the more costly ones for childbirth services. Addition Financial explains that the cost difference arises from hospital pricing in urban areas compared to rural locations. The U.S. experiences notable regional differences in childbirth expenses as three of its most expensive cities for hospital delivery are located in Florida: Tampa, Orlando, and Miami.
What Strategies Do You Need to Follow to Have a Hospital-Free Delivery Which Will Save You Money?
Parents can find alternative options that allow them to avoid large hospital fees when having a baby. Multiple options exist to help you find a more economical way to deliver your baby.
Consider Birthing Centers
Explore Payment Options at Hospitals
Check for Medicaid or Insurance Coverage
Medicaid and Insurance: You need to confirm the coverage details provided by your Medicaid or insurance plan. Many birthing centers and some hospitals accept Medicaid as payment which helps cover most of the costs.
Exploring different options allows you to select a birth plan which reflects your preferences and stays within your financial limits for a memorable yet cost-effective experience.
Challenges in the U.S. for Maternity Healthcare
Limited Insurance Coverage: Gaps in Pregnancy-Related Benefits
Many families encounter significant difficulties in childbirth preparation due to health insurance plans that provide insufficient or variable coverage.
What Insurance Often Covers
Most health insurance plans in the U.S. whether employer-sponsored or marketplace-bought normally provide coverage for standard maternity-related services.
Critical Services Often Left Out
Many plans require families to pay for additional essential services despite their offerings.
Fertility treatments (for conception): Infertility coverage exists in only 19 states yet they all have specific limitations within their policies.
The High Deductible Problem
Employer-sponsored high-deductible health plans (HDHPs) are becoming more widespread and intensify existing coverage problems. Coverage under these health plans begins only after families pay high initial expenses that frequently exceed $3,000. Many families delay essential medical care or use their savings during pregnancy because of these conditions.
Regional Disparities: Pregnancy costs and access to medical care vary greatly depending on geographic location.
The place where an individual resides significantly influences both their ability to afford pregnancy healthcare services and the accessibility of such services.
Delivery services at metropolitan hospitals typically come with higher prices because operating costs are elevated and their facilities include advanced medical technology. Vaginal deliveries in New York City urban centers reach fees above $13,000 while Cesarean sections involve prices over $16,000. The availability of private maternity rooms along with specialized care increases the overall expenses for maternity services.
Rural families face a scarcity of close maternity care facilities which has worsened due to the shutdown of numerous rural hospitals. The closure of over 140 rural hospitals throughout the U.S. between 2010 and 2024 has resulted in people living in West Texas or the Mississippi Delta losing immediate access to prenatal and delivery services. Long travel distances for medical care in these areas create dangerous delays that endanger maternal and infant health.
New York and California have implemented programs that address geographic disparities by investing in mobile clinics and telehealth services to enhance prenatal care access. These programs work to reduce healthcare access disparities facing marginalized communities.
Employer-Sponsored Plans: Addressing Gaps in Coverage
Employer-sponsored health benefits are the primary source of insurance coverage for families. Employer sponsorship leads to varying degrees of maternity-related health benefits.
Full Prenatal and Postnatal Care, Generous Parental Leave Policies.
Small employers tend to provide plans with limited coverage options which forces families to finance essential medical services like genetic screening and extended postpartum support out of pocket.
The Push for Better Maternity Benefits
The growing focus on maternal health outcomes has inspired some businesses to start providing better health benefit packages. Tech and finance firms have begun adding benefits that include:
New York: A Positive Model for Maternity Coverage
The state of New York serves as an exceptional model because its initiatives improve maternity care by addressing healthcare gaps and reducing disparities. Expecting families benefit from innovative policies which expand access to healthcare services and improve financial protection.
Expanded Medicaid Postpartum Coverage
New York extended Medicaid postpartum coverage to one year starting from 2024 as opposed to the previous 60-day limit. The policy seeks to decrease maternal mortality rates among underprivileged communities by maintaining continuous healthcare access throughout the crucial postpartum period. Expanded postpartum support enables families to more effectively manage both physical and mental health needs following childbirth.
Eligibility for Medicaid and CHIP maternity coverage relies chiefly on income levels which vary substantially between different states. State-specific guidelines and thresholds create variations in requirements across different regions of the country.
Your local Medicaid office or state health websites provide accurate information about income requirements for your situation.
First-in-the-Nation Paid Prenatal Leave
Beginning on January 1, 2025, employees in New York will receive 20 hours of paid leave each year to use for prenatal medical appointments. The policy maintains employment stability and income protection while supporting prenatal health to improve maternal and infant care.
Essential Plan: Eliminating Financial Barriers
New York's Essential Plan offers comprehensive maternity care at no cost with zero premiums and no deductibles. The 1332 State Innovation Waiver broadened eligibility to include those with incomes up to 250% of the Federal Poverty Level which supports an extra 100,000 residents. The program minimizes monetary pressure on families while providing affordable prenatal delivery and postpartum healthcare services.
Tangible Benefits of New York's Policies
These programs produced positive outcomes which included reductions in both low-birth-weight babies and preterm births. By experiencing reduced financial challenges families can better focus on health needs throughout pregnancy and its aftermath.
The active strategy adopted by New York demonstrates to other states how effective policies can close systemic healthcare gaps while promoting equal maternity care access.
Steps to Selecting the Perfect Insurance Plan for Pregnancy
When selecting a plan, families should consider:
1. Network Coverage
The insurance plan must provide access to local obstetricians, hospitals, and pediatricians.
2. Maternity-Specific Benefits
Choose insurance plans that provide comprehensive prenatal and postpartum medical services.
3. Flexibility
Select insurance options that provide telehealth services for regular appointments or consultations which proves beneficial in rural or underserved regions.
4. The Role of Employer and Private Plans
Employer-Sponsored Insurance: Convenient and often cost-effective.
Private Plans: Private plans remain the ideal choice for people lacking employer benefits because they provide customizable maternity coverage via the Health Insurance Marketplace.
Smart Approaches to Handle Prenatal and Labor Expenses When Maternity Insurance Is Unavailable
The financial obligations of prenatal and labor care become intimidating when you lack maternity insurance benefits.
These smart strategies will enable you to control your expenses:
Additional Financial Resources
Applying these financial strategies will help reduce your prenatal care and labor costs so you can concentrate more on your important upcoming life event.
Conclusion: The Value of Pregnancy Insurance
Pregnancy insurance serves as an essential health benefit which enables expecting families to receive needed medical care without facing financial difficulties. The appropriate insurance plan covers family needs throughout pregnancy and after childbirth while enhancing mothers and babies' health results.
PEO4YOU connects people to tailored health plan providers making it easier for families to discover suitable health options. PEO4YOU helps families choose maternity coverage solutions by providing comprehensive options and cost-effective private plans or employer-sponsored solutions.
A trusted partner and proper guidance enable you to fully experience parenthood by maintaining financial security and health care excellence for your family.
Recent Posts
Get In Touch— We’re available 24/7
"*" indicates required fields
“We respect your privacy. Your contact information will be used solely for the purpose of responding to your inquiry and will not be shared with third parties.”
Click To Open Modal
Get In Touch— We’re available 24/7
"*" indicates required fields
“We respect your privacy. Your contact information will be used solely for the purpose of responding to your inquiry and will not be shared with third parties.”
Thanks!
We will be in touch soon.
If you're looking to book a consultation now
Affordable health and benefits plans for small businesses, freelancers, and independent contractors.



Copyright © 2026. Peo4you. All rights reserved.