The search for health insurance presents complexity when selecting an appropriate plan that matches your personal requirements and financial constraints. Most employees choose employer-sponsored health insurance as their primary insurance option because it delivers affordable coverage and beneficial features. Employees often find understanding the complete set of employer-sponsored insurance options to be somewhat overwhelming. This article explains how provider health insurance functions through your employer alongside key features and savings techniques that assist in controlling healthcare expenses.
What is Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance?
Your employer provides you with provider health insurance as part of their benefits package for employees. This insurance provides healthcare coverage for you along with your spouse and possibly your dependents. A major benefit of employer-sponsored insurance comes from employer contributions to premium costs which result in lower rates compared to individual market plans.
Employers typically work with provider health insurance companies to offer various plans, such as:
Employees can select different types of health insurance plans which include Health Maintenance Organization (HMO), Preferred Provider Organization (PPO), and High Deductible Health Plans (HDHP). The standard practice for employees is to select from multiple available plans which best meet their personal requirements and financial capabilities. While the employer contributes to the majority of your health insurance premium, you need to cover what remains through regular payroll deductions.
How Much Do Employer Sponsored Health Insurance Plans Cost for Individual and Family Coverage Averages?
The 2024 Employer Health Benefits Survey presents data on the average yearly costs of health insurance premiums for employer-sponsored insurance plans. The average premium cost for individual health insurance coverage under employer-sponsored plans amounts to $8,951 annually for both employees and their organizations. The average annual cost for family coverage in employer-sponsored health insurance plans reaches $25,572.
Workers generally pay 16% of the insurance premium when they have single coverage in employer-sponsored plans. Employees who choose family coverage must now pay 25% towards their premium. Employers cover the leftover portion of these costs to reduce the financial burden on their employees.
Health Insurance Serves As a Fundamental Element of Employee Benefits Packages
Provider health insurance from employers forms an essential part of employee benefit packages which aim to maintain employee health while boosting satisfaction.
Benefits of Employer-Based Health Insurance
By providing streamlined access to provider health insurance companies employees can obtain top-quality healthcare coverage at reduced costs resulting in better satisfaction and productivity levels.
Understanding Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance and Tax-Advantaged Accounts for Healthcare Costs
The 2024 year brought important enhancements to Health Savings Accounts (HSAs), Health Reimbursement Arrangements (HRAs), and Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs). This section provides a summary of each plan and details the recent modifications.
Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)
High Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs) participants have access to tax-advantaged Health Savings Accounts (HSAs). These accounts permit pre-tax contributions that pay for qualified medical expenses.
Contribution Limits for 2024:
Those aged 55 or older have the option to add $1,000 to their contributions as a catch-up provision.
HDHP Requirements for 2024:
Minimum deductible: Minimum deductible requirements for 2024 stand at $1,600 for self-only coverage and $3,200 for family coverage.
The changes demonstrate attempts to remain aligned with escalating healthcare costs and inflation.
Employers fund HRAs which reimburse employees for specific healthcare costs. HRAs receive funding exclusively from employers as opposed to HSAs.
Starting from 2024 plan years employees can access up to $2,100 which reflects an increase from the previous $1,950 available in 2023.
The rise in funding enables employers to give their staff more assistance with medical costs.
Through FSAs employees can save pre-tax money to cover qualified medical expenses. FSAs remain separate from HDHPs and enforce a "use it or lose it" rule which requires participants to spend their funds during the plan year or face forfeiture.
Employees can contribute $3,200 to their health FSA salary reduction accounts which represents a $150 increase from the previous year's $3,050 limit.
The maximum amount that can be carried over for health FSAs with the carryover feature is $640 for plan years starting in 2024.
The new policies give employees enhanced flexibility to handle their healthcare spending.
Various Types of HRAs
Organizations can choose from multiple HRA options designed to match their needs and employee requirements. This overview explains the three primary HRAs and their differences.
1. Qualified Small Employer HRA (QSEHRA)
Through QSEHRAs smaller businesses have access to health reimbursement solutions which removes the need to handle complete group health insurance plans.
2. Individual Coverage HRA (ICHRA)
The ICHRA arrangement provides versatile solutions for organizations aiming to comply with ACA requirements by supporting different employee classifications.
3. Group Coverage HRA (GCHRA)
Integration: This program functions together with the employer's group health insurance plan.
Benefits: The program assists employees in paying for medical expenses that their group health plan does not fully cover including copays, deductibles, and coinsurance.
Restrictions: This reimbursement method does not apply to insurance premium costs.
GCHRA Boosts Employer Insurance by Cutting Employees' Healthcare Costs
The distinct advantages of each HRA type make them suitable for various business conditions depending on the company's size, workforce makeup, and current health coverage systems.
An analysis of health stipends reveals their function as an alternative health benefit for employees.
Employers utilize health stipends as a creative method to help employees manage healthcare expenses. Companies deliver predetermined funds to their staff to help them pay for medical expenses. Health stipends provide employees with more adaptable benefits when compared to conventional health solutions like Health Reimbursement Arrangements (HRAs).
Key Features:
No Spending Restrictions: The stipend allows employees to select any health care-related expenses for which they want to use the funds. Employees have complete freedom to decide how to spend their healthcare money whether they need doctor appointments, prescription drugs or alternative treatments.
Taxable Income: Tax authorities treat health stipends as taxable income which is an important consideration. These benefits need to be reported for tax purposes because they count as additional compensation.
How Do They Function?
Employees receive health stipends which function as additional monetary support to alleviate their medical expenses. When employers offer these benefits they show their dedication to employee health yet leave spending decisions up to the individuals. This method enables team members to manage their health choices while developing personalized health plans that meet their specific requirements.
Health stipends give employees control over their health care spending to meet their specific requirements. Employers cover the cost of health stipends yet both parties benefit from a stronger, healthier workforce.
Key Considerations
Tax Advantages: Three accounts offer advantages through pre-tax contributions and tax-free medical expense withdrawals.
Eligibility and Contributions:A person must be enrolled in a High Deductible Health Plan before they can contribute to an HSA and there are specific limits for each individual's contributions.
Employer-funded HRAs are subject to contribution limits which employers must define following IRS regulations.
Employees can contribute to FSAs up to IRS limits while employers may also choose to make contributions.
Rollover Policies: HSAs allow their funds to continue from one year to the next without any restrictions.
Employer-designed plan features determine how HRA rollover policies function
FSA funds follow the "use it or lose it" rule but certain plans provide a grace period or limited carryover option.
The 2024 updates of these accounts provide essential insights that enable efficient healthcare expense management decisions.
Why Is Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance Growing?
Recent years have seen the expansion of employer-sponsored health insurance due to multiple contributing factors. Employers expand their health insurance offerings as both a reaction to healthcare cost rises and a tactic to attract high-quality employees while keeping their workforce productive and healthy.
1. Rising Healthcare Costs
The rapid escalation of healthcare expenses serves as a primary catalyst for the expansion of employer-sponsored health insurance programs. The increasing costs of premiums combined with out-of-pocket expenses and medical treatments have led employers to offer cost-effective insurance options to their employees. Through employer-sponsored plans companies can secure group rates that are usually cheaper than individual health insurance premiums.
2. Employer Contributions to Premiums
Through substantial contributions to employees' health insurance premiums employers make their sponsored health plans significantly cheaper than personal insurance options. Employers typically fund between 50% and 80% of insurance premium costs which significantly decreases the financial responsibilities of employees. The rising cost of healthcare makes this benefit fundamental for employees which in turn increases the importance of employer-sponsored health plans.
3. Attracting and Retaining Talent
To attract and retain skilled workers in the competitive job market employers now need to provide comprehensive health coverage as a key benefit. A robust health benefits package promotes employee satisfaction while simultaneously building employee loyalty and lowering staff turnover rates. Employers acknowledge that health insurance provision has shifted from an optional benefit to an essential competitive strategy due to rising healthcare costs.
4. Tax Incentives for Employers
The U.S. government has used tax breaks to encourage employers to provide health insurance benefits to their workforce. Businesses can deduct employer contributions to employee health insurance premiums from their taxes making it an advantageous choice to provide health insurance plans. Both employers and employees benefit from this arrangement because it lowers expenses for both sides while expanding health insurance accessibility.
5. Focus on Employee Wellness
Businesses are finding that well-being in their workforce leads to higher productivity levels. The rising cost of healthcare makes providing insurance a dual advantage for companies because it serves as both a cost-saving strategy and an investment in employee health and well-being. Through coverage for preventive services and wellness programs alongside mental health support and other health benefits employees maintain their health which leads to fewer sick days and better productivity. The movement towards prioritizing employee wellness has led employers to demand more complete health insurance plans sponsored by their businesses.
PEO4YOU Provides Expert Guidance
The complicated nature of health insurance leaves many people overwhelmed yet PEO4You makes navigating it straightforward. PEO4You functions as a bridge between people and healthcare providers to find optimal healthcare plans for employees and small business owners based on their specific requirements.
How PEO4You Helps
PEO4You connects businesses and employees to healthcare solutions personalized to their requirements.
PEO4You delivers expert instructions for maximizing the use of health benefits such as HSAs, HRAs, and FSAs.
PEO4You assists businesses in negotiating superior group plans that boost employee satisfaction while reducing expenses.
PEO4You connects employers seeking advice on their sponsored plans with appropriate providers while also helping small business owners find competitive benefits solutions.
Conclusion
Employer-sponsored health insurance functions as an essential instrument for controlling growing healthcare expenses while maintaining broad access to medical services. Employees can optimize their benefits through various accounts including HSAs, HRAs, and FSAs.mize your healthcare benefits while minimizing costs.
Recent Posts
Get In Touch— We’re available 24/7
"*" indicates required fields
“We respect your privacy. Your contact information will be used solely for the purpose of responding to your inquiry and will not be shared with third parties.”
Click To Open Modal
Get In Touch— We’re available 24/7
"*" indicates required fields
“We respect your privacy. Your contact information will be used solely for the purpose of responding to your inquiry and will not be shared with third parties.”
Thanks!
We will be in touch soon.
If you're looking to book a consultation now
Affordable health and benefits plans for small businesses, freelancers, and independent contractors.



Copyright © 2026. Peo4you. All rights reserved.
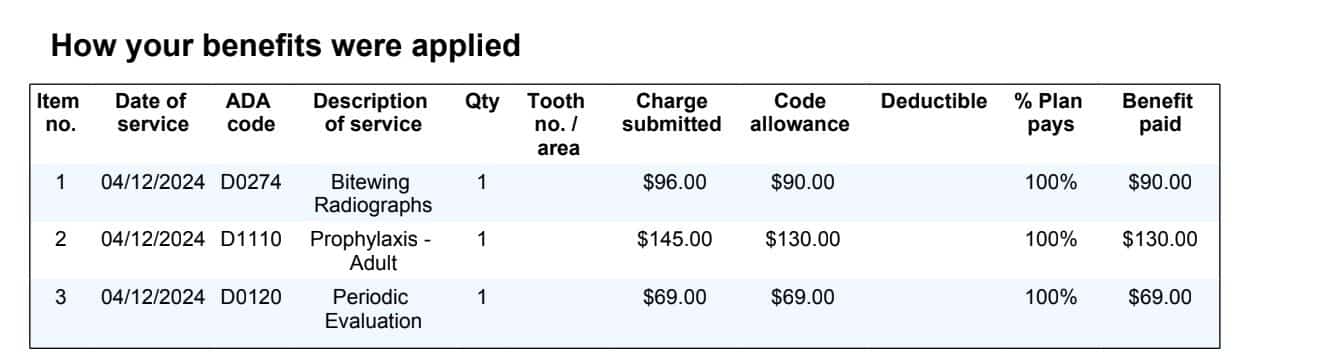









[…] Access to Care: Family members who require frequent medical attention can access their benefits sooner without waiting for the entire family deductible to be […]